Describe the Purposes and Uses of Extraoral Imaging
Radiographs provide images of larger areas such as the skull and jaw. Describe the purpose and uses of panoramic imaging 3.
Extraoral X-rays are carried out at times your dentist expects a few problems lurking in areas such as the jaws external to your teeth and gums.

. Similar to how you regularly brush and floss your teeth having done dental X-rays at a regular periodicity is also considered integral to your general oral health. Periapical receptor show the terminal end of the tooth root surrounding bone as well as the crown--parallel and bisecting technique. An help gain a better.
Describe patient preparation equipment preparation and patient- positioning procedures before exposing a panoramic projection. The purpose of this case report was to describe the treatment of a 7-year-old child who presented with an extraoral draining sinus originating from a carious developing tooth bud of the unerupted permanent mandibular left second molar. Chemical Waste Management 9 Hours Describe the components of the OSHA Hazard Communication Standard.
Typical extraoral x-ray images include panoramic cephalometric and cone beam computed tomography CBCT projections. Describe the fundamentals of panoramic imaging 4. Describe the difference between cortical and cancellous bone.
Discuss the advantages of 3D imaging. Define the key terms associated with extraoral imaging Describe the purpose and uses of extraoral imaging Describe the head position the receptor placement and beam alignment for the various extraoral images. Extraoral radiographs do not show the details as well as intraoral films do.
Define the general terms that describe prominences spaces and depressions in bone. Extraoral images are particularly beneficial for patients requiring orthodontic treatment dental implants and oral surgical procedures. In addition the use of dental imaging technology often creates a more comfortable and engaging dental visit for the patient.
Describe techniques for managing patients with physical and mental disabilities. Describe the purposes and uses of extraoral imaging. Extraoral X-rays show teeth but their main focus is the jaw and skull.
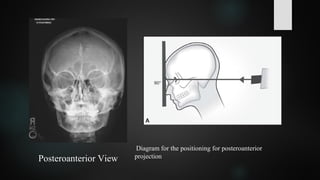
Pronounce define and spell the Key Terms. Used to image large areas of the skull or jaws. Intraoral meaning the X-ray film is inside the mouth and extraoral meaning the X-ray film is outside the mouth.
Describe the equipment used in panoramic radiography. 10 however examples are not included in this article because the diagnostic yield is poor especially compared with advanced imaging modalities and imaging of this structure is beyond what is considered dental radiography. The purpose of extra oral imaging is to view large areas of the skull or jaws and it is used to identify trauma determine size and area of lesions detect TMJ disorders diseases of the jaw and to identify location of impacted teeth.
Describe the advantages of three-dimensional 3D imaging. Describe the purpose and uses of cone beam computed tomography. Describe the equipment used in panoramic imaging 5.
The extraoral film is typically used for the following purposes 7 Evaluate large areas of the skull and jaws. Describe the equipment used in extraoral radiography. Detect diseases lesions and conditions of the jaws.
There are many types of extraoral radiographs. Contact a Rep to request more information on 3D imaging machines. Describe the purposes and uses of extraoral imaging.
Identify the core intraoral imaging techniques and list the basic rules for each. Instruction in the advanced imaging technique of the extraoral panoramic dental radiology. Gary Kaye was an early adopter of digital technology and he uses a cone beam in conjunction with same-day dentistry in his highly successful practice in Manhattan New York.
The use of dental films for extraoral imaging of the temporomandibular joint has been described. Describe purpose uses of extraoral radiography. Evaluate growth and development.
Extraoral images are acquired when the image receptor is positioned outside of the patients mouth. Describe the purposes and uses of extraoral imaging. Extraoral radiographs do not show the details as well as intraoral films.
Identify and describe the equipment used in extraoral imaging. After a thorough clinical and radiographic examination a conclusive diagnosis was determined and surgical. Extraoral radiographs are very useful for evaluating large areas of the skull and jaws but are not adequate for detection of subtle changes such as the early stages of dental caries or periodontal disease.
In the past decade digital radiography has been gaining popularity and many offices are. 1 The focus of this article will be the routine radiographs used in the dental office. Emphasis is on evaluation and interpretation of intraoral and panoramic images utilizing recognition of anatomical landmarks dental.
The Gendex GXDP-700 Series features the pinnacle of 3D dental imaging technology allowing dentists to plan for more predictable treatment outcomes by taking advantage of powerful 3D software analysis and simulation tools. Describe the purpose of the different extraoral film projections. There are two main types of dental X-rays.
The cone beam computed tomography is used to view the area of the head and neck in three dimensions and it is used to find the exact placement of implants the buccallingual position of impacted teeth to be removed and determination of the exact location of the mandibular nerve before surgery is done. Prepare the equipment and the patient for a panoramic procedure and produce an image. Identify and discuss anatomical landmarks for proper mounting of radiographs as required by the dentist.
Define extraoral radiography and apply extraoral radiographic techniques. Describe the patient and equipment preparation that are necessary before exposing an extraoral film. Intraoral X-rays are the most common type of dental X-ray taken.
More recent innovations include the use of digital CT scans and 3D imaging in the dental office similar to CT scans done in hospitals and medical imaging centers. Describe the equipment used in extraoral imaging. Extraoral radiographs are useful in evaluating large areas of the skull and jaws but are not adequate for detection of subtle changes such as the early stages of dental caries or periodontal disease.
Describe the purpose type of receptor and technique used for each of the 3 types of intraoral radiographic examinations. There are many type of extraoral radiographs. Describe the purpose and uses of panoramic radiography.

Pdf Intraoral Versus Extraoral Bitewing Radiography In Detection Of Enamel Proximal Caries An Ex Vivo Study

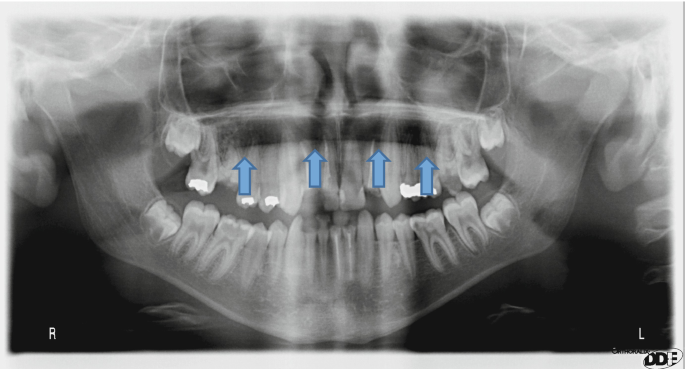
Landmarks And Interpretation In Extraoral Radiography
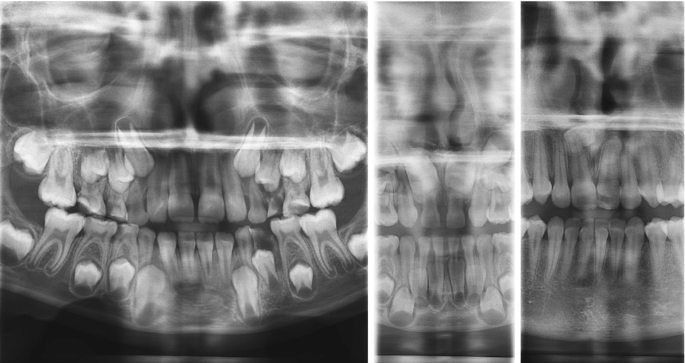
Extraoral Radiography In Pediatric Dental Practice Springerlink

Extraoral Radiographic Projections Topics In Description Below Youtube
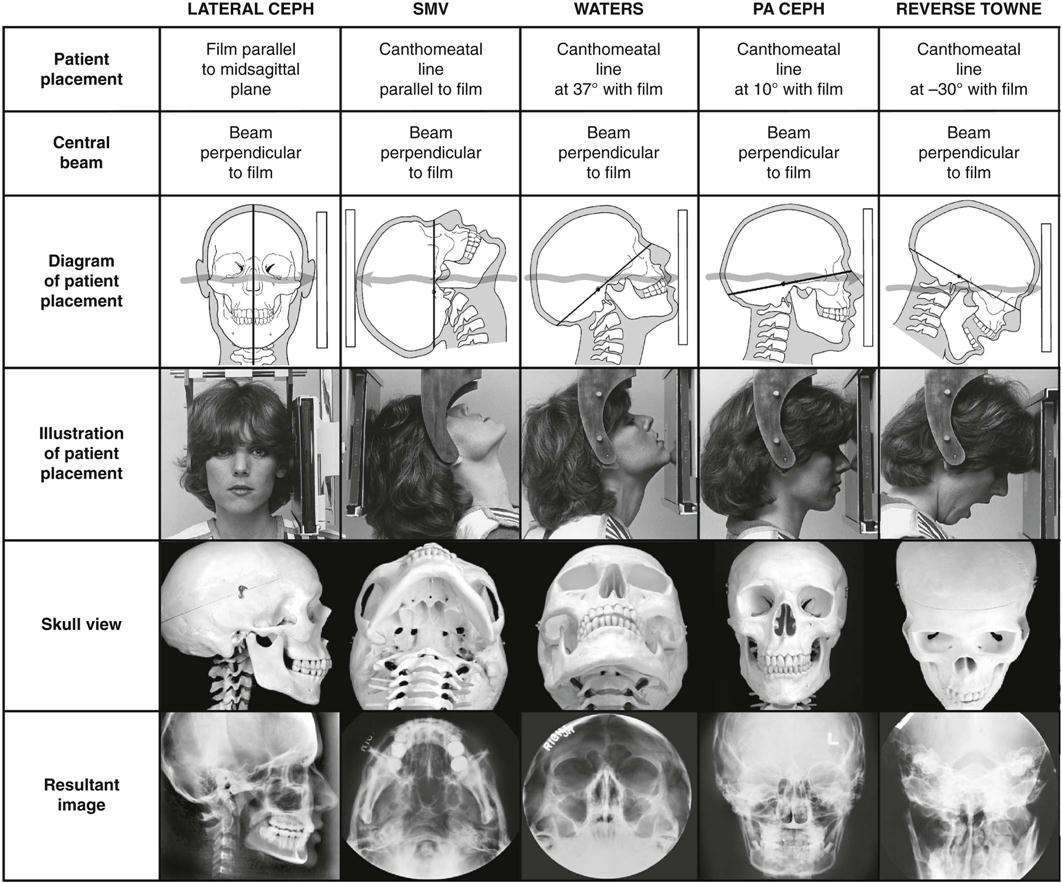
9 Extraoral Projections And Anatomy Pocket Dentistry

Types Of Dental Radiographs And Their Uses Dentalnotebook

Extraoral Surgical Access For Removal Of Intraparotid Giant Sialolith In Young Patient A Case Report Revista Espanola De Cirugia Oral Y Maxilofacial
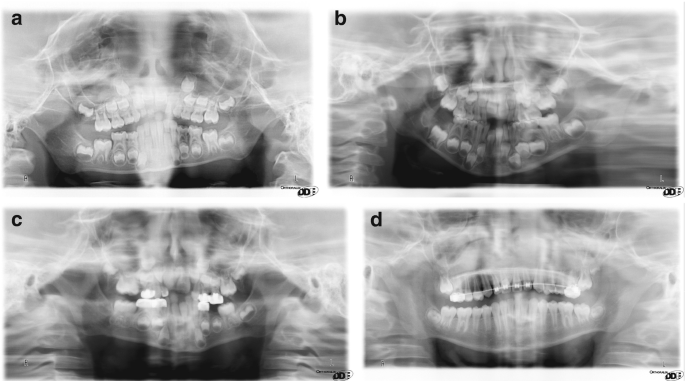
Patient Movement Artefact Correction For Cbct Images Planmeca
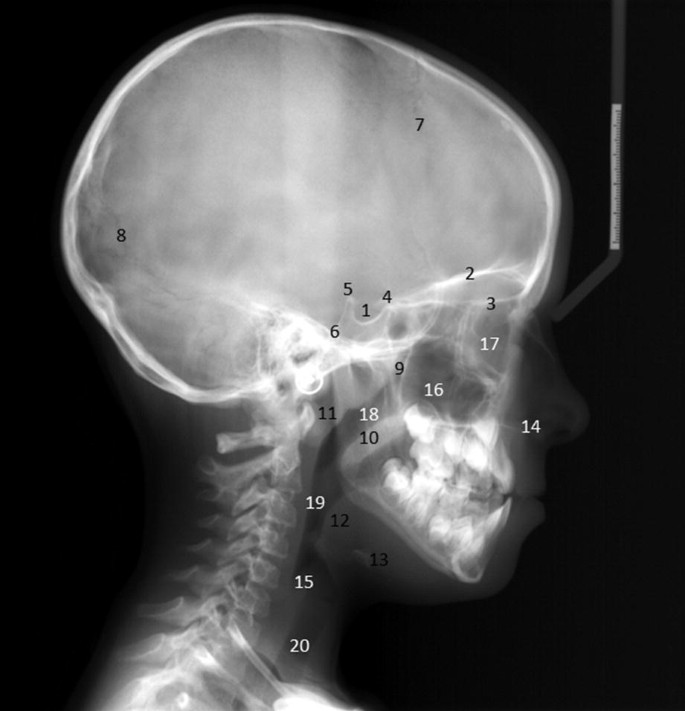
Landmarks And Interpretation In Extraoral Radiography
Extraoral Radiography In Pediatric Dental Practice Springerlink

Chp 42 Extraoral Imaging Flashcards Quizlet

Panoramic Radiography For The General Practitioner Oral Health Group

Cassette Screens Film X Rays Cassette Front Foam Rigid Cassettes Screen Support Phosph Film Ray Film Screen Film


Comments
Post a Comment